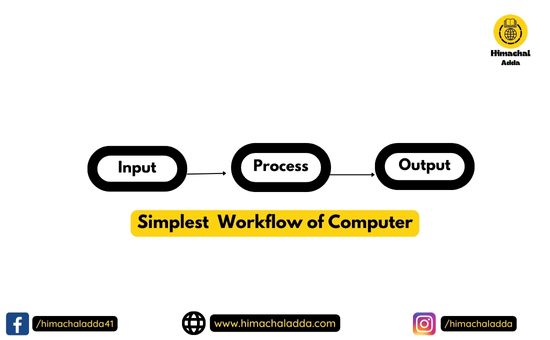
Introduction to Computer:- The term computer is derived from the latin word ‘computare’ which means ‘to compute’. The literal meaning of computer is a device that can calculate. However, modern computers can do a lot more than calculate. Computer is an electronic device that receives input, stores or processes the input as per user instructions and provides output in desired format.
What is Computer?
A computer is a programmable electronic device that accepts raw data as input and processes it with a set of instructions (a program) to produce the result as output.
It is believed that the Analytical Engine was the first computer which was invented by Charles Babbage in 1837. It used punch cards as read-only memory. Charles Babbage is also known as the father of the computer.
The basic computer parts are as follow:
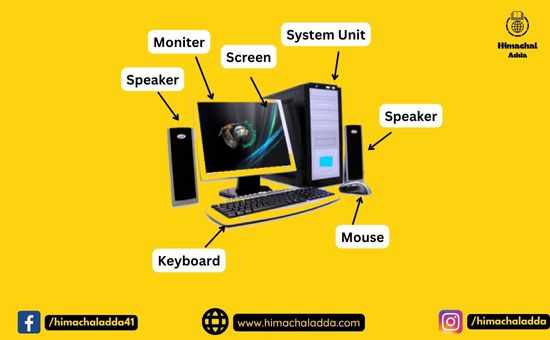
1)Input unit : Input Unit consists of input devices such as keyboard, mouse etc. These devices are used to input information and instruction into computer system.
2) CPU(Central Processing Unit) – CPU is also called the brain of computer system. It is an electronic hardware device that processes all the operations(e.g. arithmetic and logical operation) of the computer.CPU is responsible for handling the operations of several others units.
Control unit and ALU (Arithmetic and Logical Unit are jointly called the Central Processing Unit (CPU).
a) Control Unit− As the name suggests, this unit controls all the functions of the computer. All devices or parts of computer interact through the control unit.
b) Arithmetic Logic Unit(ALU)– ALU performs arithmetic operations and logical operations.ALU controls simple operations such as addition, subtractions, division and multiplication.
3)Memory Unit : Memory unit is an essential part of computer system which is used to store data and instructions before and after processing.
There are two types of Memory
1)Primary Memory – it is also called an main memory or Temporary memory. The data stored in primary memory are temporary. The data will be lost if they are disconnected from the power supply. Primary memory cannot store a large amount of data. It usually stores the input data and immediate calculation results. Random access memory (RAM) is an example of Primary Memory.
2) Secondary Memory : it is also called permanent storage or auxiliary storage. In this memory data is stored permanently for future use. The data stored in the secondary memory is safe when there is power failure or no power supply. Hard disk is an example of secondary memory
Output Unit : Output units consists of devices that are used to display the results or output of processing. The output data is firstly stored in the memory and then displayed in human –readable form though output devices like Monitor, Printer etc.
History of Computer
The first counting device was used by the primitive people. They used sticks, stones and bones as counting tools.. Some of the popular computing devices starting with the first to recent ones are described below;
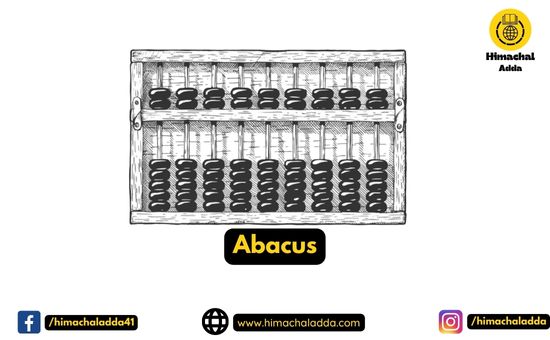
Abacus
- The history of computer begins with the birth of abacus which is believed to be the first computer.
- It is said that Chinese invented Abacus around 4,000 years ago.
- It is the first mechanical device
- It used for addition and subtraction.
Napier’s Bones
- It was invented by John Napier (1550-1617) of Merchiston.
- Holding numbers from 0 to 9 only.
- It perform multiplication on numbers.
- It was also the first machine to use the decimal point.

Pascaline
- Pascaline is also known as Arithmetic Machine or Adding Machine.
- It was invented between 1642 and 1644 by a French mathematician-philosopher Blaise Pascal.
- It is believed that it was the first mechanical and automatic calculator.
- It perform addition and subtraction of two numbers

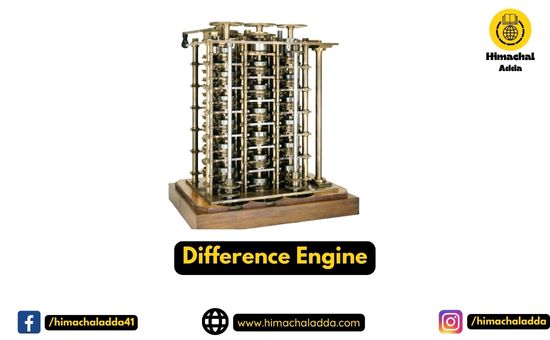
Difference Engine
- In the early 1820s, it was designed by Charles Babbage who is known as “Father of Modern Computer”.
- It was a mechanical computer which could perform simple calculations.
Analytical Engine
- It was also developed by Charles Babbage in 1830-1840.
- It was a mechanical computer that used punch-cards as input.
- It generally used for basic arithmetic operations.
- It was a decimal machine used sign and magnitude for representation of a number.
Tabulating Machine
- It was invented, by Herman Hollerith, an American statistician.
- It used punched cards with round holes.
- It was a first electromechanical machine, which was designed to process the data for census in 1890.
- Hollerith also started the Hollerith’s Tabulating Machine Company which later became International Business Machine (IBM) in 1924.

Differential Analyzer
- It was the first electronic computer introduced in the United States in 1930.
- It was an analog device invented by Vannevar Bush.
- This machine has vacuum tubes to switch electrical signals to perform calculations.
- It could do 25 calculations in few minutes.

Mark I
- It was invented by Howard Aiken in 1944.
- In this machine data can be entered manually.
- It was mainly used in the war effort during World War – II
- In 1944, Mark I computer was built as a partnership between IBM and Harvard.
- It was the first programmable digital computer.

Atanasoff-Berry Computer(ABC)
- It was First Un-Programmable Electronic Digital Computer
- It was designed by John Vincent Atanasoff and Clifford Berry .
- It was designed to solve system of linear algebraic equations.
- It was also the first to use capacitor for storage.

ENIAC ( Electronic Numerical Integrator and Computer)
- It was developed by JP Eckert and JW Mauchly in 1946.
- ENIAC is the first electronic digital Computer.
- It was used for weather predictionary atomic energy calculation and other scientific uses.

EDVAC ( Electronic Discrete Variable Automatic Computer)
- It was developed by John Von Neumann in 1949.
- It was the first computer which provided storage capacity.
- It was capable of storing instruction and data in memory.

UNIVAC( Universal Automatic Computer)
- It was developed by JP Eckert and JW Mauchly in 1951.
- It was the first general purpose electronic with large amount of input and output.
- It used magnetic tapes as input and output.

Generation of Computer
First Generation(1946-1959)
- In these computers, vacuum tubes were used as the basic components of CPU and memory.
- This Generation computers relied on Machine Language (Binary number 0s and 1s)
- These computers were mainly depended on batch operating system and punch cards.
- Magnetic tape and paper tape were used as output and input devices in this generation.
- They were huge in size and occupied almost a room-size area to fit in.
Examples of computers developed in this generation are:-
- ENIAC – Electronic Numeric Integrated and Computer
- UNIVAC- Universal Automatic Computer
- EDSAC – Electronic Delay Storage Automatic Calculator
- EDVAC – Electronic Discrete Variable Automatic Computer
- IBM-701
- IBM-650
Second Generation Computers(1959-1965)
- The second generation was the era of the transistor computers.
- These computers used transistors which were cheap, compact and consuming less power; it made transistor computers faster than the first generation computers.
- Assembly language and programming languages like COBOL and FORTRAN were used in these computers.
- In this generation Time sharing and multitasking operation system are used.
- Magnetic cores were used as the primary memory and magnetic disc and tapes were used as the secondary storage.
Some of the popular second generation computers are;
- IBM 1620
- IBM 7094
- CDC 1604
- CDC 3600
- UNIVAC 1108
Third Generation Computers (1965-1971)
- The third generation computers used integrated circuits (ICs) instead of transistors.
- These generation computers used remote processing, , multi programming ,real-time system as operating system.
- The high-level programming languages like FORTRONCOBOL, PASCAL PL/1, ALGOL-68 were used in this generation.
Some of the popular third generation computers are;
- IBM-360 series
- Honeywell-6000 series
- PDP(Personal Data Processor)
- IBM-370/168
- TDC-316
Fourth Generation Computers(1971-1980)
- The fourth generation) computers used very large scale integrated (VLSI) circuits; a chip containing millions of transistors and other circuit elements.
- These generation computers used real time, time sharing and distributed operating system.
- All the high-level languages like C, C++, DBASE etc., were used in this generation.
Some of the popular fourth generation computers are;
- DEC 10
- STAR 1000
- PDP 11
- CRAY-1(Super Computer)
Fifth Generation Computers
- The VLSI technology was replaced with ULSI (Ultra Large Scale Integration)in this generation.
- It made possible the production of microprocessor chips with ten million electronic components.
- This generation computers used parallel processing hardware and AI (Artificial Intelligence) software.
- The programming languages used in this generation were C, C++, Java, .Net, etc.
Some of the popular fifth generation computers are;
- Desktop
- Laptop
- NoteBook
Points to be Remember
- Charles Babbage is known as the father of computer.
- Alan turning is known as the father of modern computer.
- First non-programmable electronic digital computer –Atanasoff Berry Computer (ABC)
- First general purpose electronic digital computer – ENIAC
- First Commercially available computer – UNIVAC
- First Micro Processer – Intel 4004




