Ch-5 Html Fundamentals
Q1) Define HTML and explain the structure of HTML?
HTML, which stands for HyperText Markup Language, is the standard language used to create and design web pages. It provides the structure of a webpage, allowing the embedding of text, images, links, and other elements. HTML uses a system of tags to organize and format the content.
Structure of HTML
A simple HTML document includes the following components:
<html>
<head>
<title>Page Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>My First Heading</h1>
<p>My first paragraph.</p>
</body>
</html>
- The <html> tag is the root element of an HTML document. All other elements are nested inside this tag.
- The <head> element contains meta-information about the document, such as the title, character set, styles, and links to external resources.
- The <body> element contains the content of the HTML document, such as text, images, links, and other media. This is where most of the visible content is defined.
Q2) What do you mean by Tag? Explain container and empty tag?
In HTML, a tag is a component used to create elements and structure content on a webpage. Tags are enclosed in angle brackets (< >) and typically come in pairs: an opening tag and a closing tag. The content lies between these tags.
Types of Tags
- Container Tags :Container tags are tags that surround and contain content. They have both an opening tag and a closing tag.
Structure of Container tags:
<tagname>Content</tagname>
Heading tag(<h1> to <h6>), paragraphs (<p>), text formatting (<b> for bold, <i> for italic), hyperlinks (<a>), etc.are example of Container tag.
- Empty Tags : Empty tags do not contain any content and do not require a closing tag. They are also known as self-closing tags.
Structure Empty tags:
<tagname />
<img> (for images), <br> (line break), and <hr> (horizontal rule) are example of empty tag.
Q3) How can you insert an image in webpage?
To insert an image into a webpage using HTML, we use the <img> tag. The <img> tag is an empty (self-closing) tag, meaning it does not require a closing tag.
Example of Inserting an Image:
Assuming the image file picture.jpg is in the same directory as your HTML file:
<html>
<head>
<title>Image Example</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Welcome to My Webpage</h1>
<p>Here is an image:</p>
<img src="picture.jpg" alt="A beautiful scenery" width="600" height="400">
</body>
</html>
Image Attributes:
- src (source): This attribute specifies the URL of the image we want to display.
- alt (alternative text): This attribute provides a text description of the image, which is used by screen readers for accessibility and displayed if the image cannot be loaded.
- width and height: These attributes specify the dimensions of the image in pixels.
Q4) How would you insert background picture in web page?
To insert a background picture on a webpage, we can use the deprecated HTML background attribute on the <body> tag.
<html>
<head>
<title>Background Image Example</title>
</head>
<body background="desktop/images/image.jpg ">
<h1>Welcome to My Webpage</h1>
<p>This webpage has a background image.</p>
</body>
</html>
The background attribute is used within the <body> tag to specify the path to the background image.
Q5) What is the purpose of tag?
The <p> tag in HTML is used to define a paragraph of text. It is a block-level element, meaning it typically starts on a new line and creates a block of content. The purpose of the <p> tag is to structure and format text content into distinct paragraphs, making the text more readable and organized.
Basic Syntax:
<p>This is a paragraph of text.</p>
Example :
<html >
<head>
<title>Paragraph Example</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Welcome to My Webpage</h1>
<p>This is the first paragraph. It provides an introduction to the content of the webpage.</p>
</body>
</html>
Q6) What are the attributes of tag?
The <font> tag in HTML is used to define the font face, font size, and color of text.
Attributes of the <font> Tag
- color: Specifies the color of the text.
- face: Specifies the font family for the text.
- size: Specifies the size of the text.
Example:
<html>
<head>
<title>Font Tag Example</title>
</head>
<body>
<font color="red" face="Arial" size="4">
<p>This is a paragraph with specified font attributes using the Font tag.</p>
</font>
</body>
</html>
Q7) How can you insert paragraph break?
To insert a paragraph break in HTML, we can use the <br> tag. Simply add it wherever we want a line break within your content. For example:
<html>
<head>
<title>Line Break Example</title>
</head>
<body>
<p>This is the first line.<br>This is the second line.<br>This is the third line.</p>
</body>
</html>
Output
This is the first line
This is the second line.
This is the third line.
Q8) What is the purpose of tag?
The <BASEFONT> tag in HTML was used to set a default font size, color, and face for the text within an HTML document. However, this tag is deprecated and is no longer supported in modern HTML standards. Its purpose was to provide a way to specify a base font for the entire document, so that all the text would inherit these properties unless overridden by other tags or styles.
Attributes of <BASEFONT> Tag:
- size: Specifies the base font size. It can be an absolute size (1 to 7) or a relative size (+1, -1, etc.).
- color: Specifies the color of the text.
- face: Specifies the font face (typeface) to use.
Example :
<basefont size="4" color="red" face="Arial">
<p>This is some text.</p>
<p>This is some more text.</p>
Q9) How can you add comments to HTML document?
In HTML, comments can be added using the following syntax:
<!– This is a comment –>
Comments are useful for explaining the code, making notes, or temporarily disabling code without deleting it. They are not displayed in the browser and are ignored during the rendering of the page.
Example :
<html >
<head>
<title>Comment Example</title>
</head>
<body>
<!-- This is a single-line comment -->
<p>This is a paragraph.</p>
<!--
This is a multi-line comment.
It can span multiple lines.
-->
<p>This is another paragraph.</p>
</body>
</html>
Q10) What is the purpose of tag in HTML? Explain.
The <HR> tag in HTML stands for “Horizontal Rule” and is used to create a horizontal line across the web page. This line serves as a thematic break or a visual separator between different sections of content.
Example:
<html>
<head>
<title>HR Tag Example</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Title of the Document</h1>
<p>This is the first paragraph of the document.</p>
<hr>
<h2>Subsection</h2>
<p>This is a new section of the document.</p>
</body>
</html>
Output
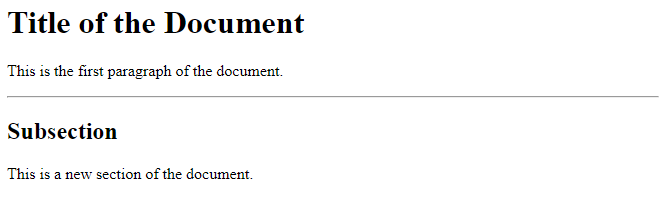
Q11) Show the use of Heading tags in HTML with example?
Heading tags in HTML are used to define headings and subheadings within a web page. They range from <h1> to <h6>, with <h1> being the highest or most important level and <h6> being the lowest or least important level. Headings help organize content, making it easier for users to read and for search engines to understand the structure of the page.
Example of Heading Tags:
<html>
<head>
<title> Example of Heading tags </title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Heading 1</h1>
<h2>Heading 2</h2>
<h3>Heading 3</h3>
<h4>Heading 4</h4>
<h5>Heading 5</h5>
<h6>Heading 6</h6>
</body>
</html>
Output

Q12) What are different style tags in HTML?
HTML provides various style tags, which are as follows:
- Bold Text: To make text bold, you can use the <b> or <strong> tags. The <b> tag simply applies a bold styling to the text, while the <strong> tag also indicates that the text is of strong importance.
- Italic Text: To italicize text, you can use the <i> or <em> tags. The <i> tag simply applies an italic styling, while the <em> tag indicates that the text should be emphasized, often resulting in italicized text as well.
- Underlined Text
To underline text, you can use the <u> tag. This tag applies an underline styling to the text.
Example :
<html>
<head>
<title>Style tag Example</title>
</head>
<body>
<p>This is a <b>bold</b> text using the <b> tag.</p>
<p>This is an <i>italic</i> text using the <i> tag.</p>
<p>This is an <u>underlined</u> text using the <u> tag.</p>
</body>
</html>
Output
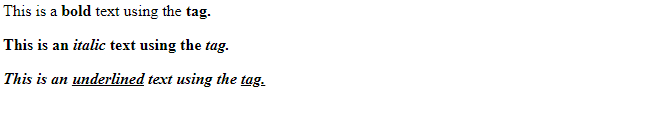
Q13) What do you mean by List? What are various type of list in HTML?
In HTML, a list is a collection of related items that are grouped together in a structured format. Lists are used to present information in a readable and organized manner. There are three main types of lists in HTML:
- Unordered List (<ul>):
An unordered list is a list of items where the order does not matter. The items in an unordered list are typically marked with bullet points.
- Ordered List (<ol>):
An ordered list is a list of items where the order does matter. The items in an ordered list are typically marked with numbers or letters.
- Definition List (<dl>):
A definition list is used for defining terms. It consists of pairs of terms and descriptions.
Example :
<html>
<head>
<title>HTML lists</title>
</head>
<body>
<!-- Ordered List -->
<ol>
<li>First item</li>
<li>Second item</li>
</ol>
<!-- Unordered List -->
<ul>
<li>Bullet item</li>
<li>Another bullet item</li>
</ul>
<!-- Description List -->
<dl>
<dt>Term 1</dt>
<dd>Description for term 1</dd>
<dt>Term 2</dt>
<dd>Description for term 2</dd>
</dl>
</body>
</html>
Output

Q14) What is hyperlink? What are various links in HTML? Explain.
A hyperlink, or simply a link, in HTML is an element that allows users to navigate from one web page or resource to another. Links are fundamental to the web’s structure, enabling the creation of interconnected documents.
Creating a Hyperlink
Hyperlinks are created using the <a> (anchor) tag. The href attribute of the <a> tag specifies the destination of the link.
Example:
<html>
<head>
<title>Hyperlink Example</title>
</head>
<body>
<p>Visit <a href="https://www.example.com">Example Website</a>.</p>
</body>
</html>
Types of Links in HTML
- External Links: These links point to pages or resources on different websites.
Example:
<a href=”https://www.google.com”>Go to Google</a>
- Internal Links: These links point to other pages or resources within the same website.
Example:
<a href=”/about.html”>About Us</a>
- Anchor Links (or Fragment Links): These links point to specific parts of the same page or another page. They use the # symbol followed by an identifier that matches an id attribute in the HTML.
Example:
<a href=”#section2″>Go to Section 2</a>
<!– Somewhere else in the document –>
<h2 id=”section2″>Section 2</h2>
- Email Links: These links open the user’s email client with a pre-filled email address.
Example:
<a href=”mailto:someone@example.com”>Send Email</a>
- Telephone Links: These links initiate a phone call when clicked on devices that support calling.
Example:
<a href=”tel:+1234567890″>Call Us</a>
- Download Links: These links allow users to download a file. You can suggest the browser to download the file by adding the download attribute.
Example:
<a href=”files/document.pdf” download>Download PDF</a>
Q15) How can you create table in HTML?
To create a table in HTML, you use the <table> tag along with <tr> for table rows, <th> for table headers, and <td> for table data cells. Here’s a simple example:
Output
<html>
<head>
<title> Creating Table</title>
</head>
<body>
<h2>HTML Table</h2>
<table border ="2">
<tr>
<th>Roll No.</th>
<th>Name</th>
<th>Class</th>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>1101</td>
<td>Vishal</td>
<td>12th</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>1102</td>
<td>Rohin</td>
<td>11th</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>1103</td>
<td>Ajay</td>
<td>10th</td>
</tr>
</table>
</body>
</html>

Q16) What is the difference between and tag?
The <td> (table data) tag is used for standard cells in the table which contain data, while the <th> (table header) tag is used for cells that contain header information.
- <th> elements are bold and centered by default.
- <td> elements are regular weight and aligned to the left.
Here’s an example to illustrate:
<html>
<head>
<title> Creating Table</title>
</head>
<body>
<table>
<tr>
<th>Header 1</th> <!-- This is a header cell -->
<th>Header 2</th> <!-- This is another header cell -->
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Data 1</td> <!-- This is a data cell -->
<td>Data 2</td> <!-- This is another data cell -->
</tr>
</table>
</body>
</html>
Output





