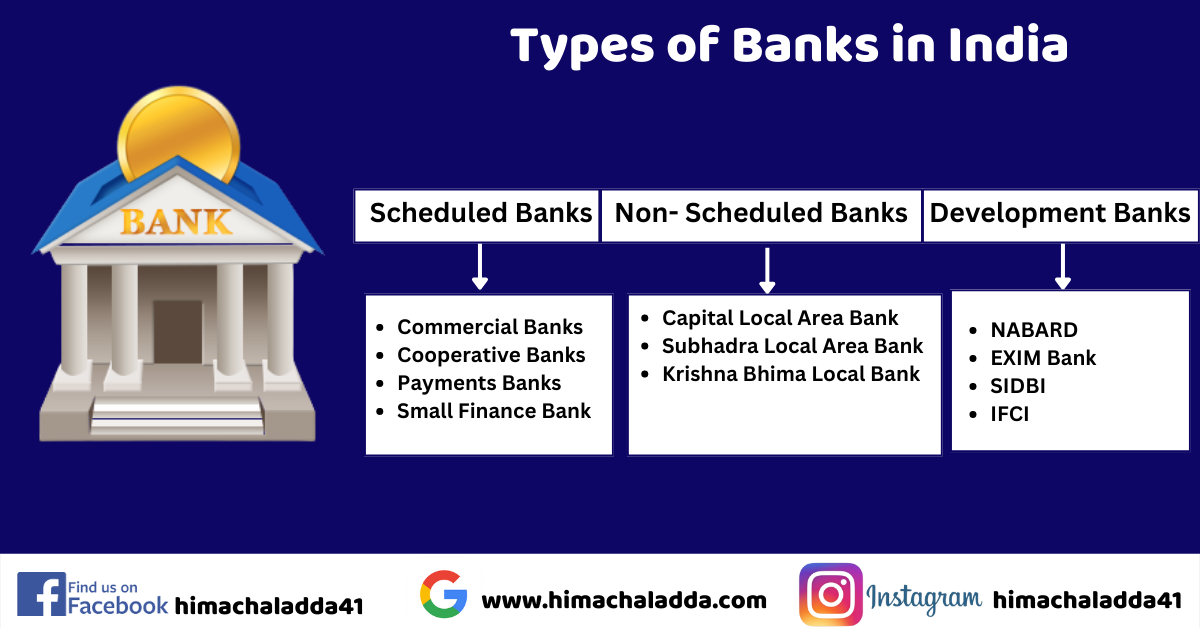
Types of Banks in India
Before studying the classification of banks in India first we should understand the bank. Banks are financial institutions that perform deposits and lending of money.
There are various types of banks in India and each is responsible to perform different functions as per the formation and guidance of RBI, which reflects that India is a mixed economy.
The banking system is a core pillar of any nation’s economy. For that, each country has a central bank that regulates the banking system by controlling all banks in that country.
Banks are classified into various types. Given below are the types of Banks in India:

Reserve Bank of India
The banking system is being regulated by the central bank of India, RBI (Reserve Bank of India). RBI is the Central Bank of our country, which was established on 1st April 1935 under the RBI Act, 1934. It holds the top position in the Structure of the Indian Banking System.
Read More : History of RBI
Given below are the functions of the Reserve Bank of India
- Financial Supervision
- Regulator and supervisor of the financial system
- Issue of currency
- Regulator of the Banking system
- Banker and debt manager to government
- Banker’s Bank
- Implementing the monetary policies
- Custodian to Foreign exchange
- Monitoring of all different types of banks in India.
Scheduled Banks
Scheduled Banks are the banks that are listed in the second schedule of the RBI Act, 1934 Section 2(e). In the second schedule, only those banks are get listed that satisfy the criteria of RBI Act 1934, Section 42.
• These banks automatically get clearinghouse membership
• The RBI allows scheduled Banks to raise debts and loans at bank rates
In order to be listed in the second schedule of RBI Act, a bank must satisfy the following eligibility criteria:
a) The paid up capital and reserve together should be not less than INR 5 Lakh.
b) Working of the bank should be detrimental to the interest of the depositors.
c) They should either be a company as per the Companies Act 1956 or a State Cooperative Bank or a Corporation or any institution notified by the government of India.
In this regard every week , the Scheduled bank have to provide the details of their activities to the RBI.
All 4 types of banks in India commercial banks, co-operative banks, small finance banks, and payment banks, fall under the scheduled bank’s category. All 4 types of banks are members of the RBI clearinghouse.
Scheduled bank classification in India into:
1. Commercial banks
2. Co-operative banks
3. Small finance banks
4. Payments banks
Commercial banks
1. Commercial banks – A commercial bank is a kind of financial institution that carries all the operations related to deposit and withdrawal of money for the general public, providing loans for investment, and other such activities. These banks are profit-making institutions and do business only to make a profit.
Commercial banks are divided into:
I. Public Sector Banks
II. Private Sector Banks
III. Regional Rural banks
IV. Foreign Banks
I. Public sector bank:
Refer to a type of commercial banks that are nationalized by the government of a country. In public sector banks, the major stake is held by the government. In India, public sector banks operate under the guidelines of Reserve Bank of India (RBI), which is the central bank
II. Private Sector Banks
Banks in which a major stake or equity is held by private shareholders. All the banking rules and regulations laid down by the RBI will be applicable to private sector banks as well.
III. Regional Rural Bank
Regional Rural Banks (RRBs) are government owned scheduled commercial banks of India that operate at regional level in different states of India. These banks are under the ownership of Ministry of Finance , Government of India. They were created to serve rural areas with basic banking and financial services. However, RRBs also have urban branches.
The authorized capital of Regional Rural Banks is Rs. 5 crores which is contributed by Central Government, State Government and the Sponsor Bank in ratio of 50:15:35.
IV. Foreign Banks
Foreign banks are registered and have their headquarters in another country, but they have branches in our country. A foreign bank branch is a type of foreign bank that is required to follow both the home and host country’s regulations. Banks frequently open a foreign branch in order to better serve their multinational corporate clients.
Cooperative Banks
Co-operative bank was set up by passing a co-operative act in 1904. They are organised and managed on the principal of co-operation and mutual help. The main objective of co-operative bank is to provide rural credit.
They can be divided into two types, which can further be subdivided:
- Urban Co-operative Banks
- Rural Co-operative Banks
Payment Bank
3) Payment Bank : Payment bank is generally a non-full service niche bank in India. It is a distinguished bank that will undertake only limited banking functions which are allowed as per the Banking Regulation Act of 1949.
The licenced entities as payment banks could only receive deposits and offer remittances. They cannot undertake lending activities. The main objective of the payment banks is to increase financial inclusion by offering small saving accounts and payment remittance services to users.
Small finance banks
4) Small finance banks – Small finance banks are a type of niche banks in India. Banks with a small finance bank license can provide basic banking service of acceptance of deposits and lending. The aim behind these is to provide financial inclusion to sections of the economy not being served by other banks, such as small business units, small and marginal farmers, micro and small industries and unorganised sector entities
Non-scheduled banks
- Non-scheduled banks, by definition, are those that do not adhere to the RBI’s regulations. They are not mentioned in the Second Schedule of the RBI Act, 1934, and are therefore deemed incapable of serving and protecting depositors’ interests.
- Non-scheduled banks must also meet the cash reserve requirement, but not with reserve banks, but with themselves. They are generally smaller in size and have a range of influence that is somewhat narrow. They are risky to do business with due to their financial limitations. The reserve capital of these banks is less than 5 lakh rupees.
- Except in emergencies, non-scheduled banks are not eligible for Reserve Bank financial assistance. Non-schedule banks are often denied the benefits enjoyed by scheduled banks. They are also not eligible to be a member of a clearinghouse. As a result, unscheduled banks cannot facilitate interbank financial transactions and the clearance of cheques.
- They are generally smaller in size and have a range of influence that is somewhat narrow. They are risky to do business with due to their financial limitations. The reserve capital of these banks is less than 5 lakh rupees.
- There are 10 Non-Scheduled State Cooperative Banks as described by RBI. Furthermore, 1458 Non-Scheduled Urban Co-operative Banks as described by RBI.
These three local area banks fall under Non- Schedule Banks:
a) Coastal Local Area Bank Ltd – Vijayawada (Andhra Pradesh)
b) Krishna Bhima Samruddhi Local Area Bank Ltd, Mahbubnagar (Andhra Pradesh)
c) Subhadra Local Area Bank Ltd., Kolhapur (Maharashtra)
Scheduled and Non-Scheduled banks:
A bank is said to be a scheduled bank when it has a paid up capital and reserves as per the prescription of RBI and included in the second schedule of RBI Act 1934. Non-scheduled bank are those commercial banks, which are not included in the second schedule of RBI Act 1934.
Comparing Scheduled Banks and Non-Scheduled Banks
Difference | Scheduled Banks | Non-Scheduled Banks |
Second Schedule | They are listed in the second schedule. | Banks are not mentioned in the second schedule. |
Meaning | A Scheduled bank is a banking company with a paid-up capital of Rs. 5 lakhs or more. | Non-scheduled banks, on the other hand, are those that are unable to comply with the RBI's requirements. |
Cash Reserve Ratio | Reserve Bank of India | They maintain with themselves. |
Borrowing | They are authorized to borrow funds from the Reserve Bank of India. | They are not authorized to borrow money from the Reserve Bank of India. |
Risk | They are financially stable and are unlikely to hurt the rights of the depositors | These banks are riskier to do business |
Returns | They are required to file their returns on a periodic basis. | There is no such clause. |
Membership | They can apply to join the clearinghouse | Are not eligible for membership in the clearinghouse |
Examples | Commercial Banks, Private, and Public sector Banks | Local banks, State Cooperative Banks |
Development banks
Development banks
Development banks are financial institutions (DFIs) that provide long-term credit for capital-intensive investments with long payback periods, such as urban infrastructure, mining and heavy industry, and irrigation systems.
It lays the foundation for industrial growth and development in the country.
Some of them are,
1) Industrial Finance Corporation of India (IFCI)
Industrial Finance Corporation of India (IFCI) is actually the first financial institute the government established after independence. The main aim of the incorporation of IFCI was to provide long-term finance to the manufacturing and industrial sector of the country.
2) Small Industries Development Bank of India (SIDBI)
The SIDBI was established as a wholly owned subsidiary of Industrial Development Bank of India (IDBI) under a special Act of the Parliament 1988 and started its operations on April 2, 1990.Small Industries Development Bank of India (SIDBI) is the apex regulatory body for overall licensing and regulation of micro, small and medium enterprise finance companies in India.
3)Export and Import Bank of India (EXIM)
Exim Bank was established in 1982 under the Export-Import Bank of India Act 1981 as a purveyor of export credit. R.C. Shah was the bank’s first Chairman and Managing Director.
4) National Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development (NABARD)
National Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development was established in 1982 on the recommendation of B. Sivaraman Committee for the overall regulation and licensing of regional rural banks and apex cooperative banks in India.
5) National Housing Bank
National Housing Bank (NHB), is the apex regulatory body for overall regulation and licensing of housing finance companies in India. It is under the jurisdiction of Ministry of Finance , Government of India